Introduction
What Is Static Electricity?
All objects, either conductive or non-conductive, have an electric charge. Objects that are connected to each other by a good conductor have the same electric charge. Objects that are connected to each other by a good conductor have the same electric charge, at least at a point near the connection. Objects with the same electric charge cannot produce an electrostatic discharge (ESD), i.e., a spark.
Static electricity refers to the presence of a non-neutral electric charge on an object. This charge can either be positive, meaning the object has more protons than electrons, or negative, meaning the object has more electrons than protons. Static electricity can be created when two objects of different material come into frictional contact, resulting in an exchange of electrons known as the triboelectric effect.
If given the opportunity, a more negatively charged object will want to send its excess of electrons to a more positively charged object, in such a way as to equalize the charges of both objects. This is analogous to how a liquid in a container will want to flow down to a container that is beneath it. If both containers are on a level surface with a pipe between them, then the level of liquid will equalize in each container. The same thing happens when two objects are electrically bonded together--both objects equalize to the same electrical charge.
The difference in charge between two objects directly relates to a quantity called electric potential difference, or voltage, measured in volts (V). The bigger the difference in charge, the higher the voltage, and the more energy will be released in an electrostatic discharge. The potential difference can be compared to the height of one water container above another--the higher the water falls, the more kinetic energy it has when it reaches the second container.
Static Electricity Hazards In Industry
It is common in industrial processes for potential to be more than 30 kV (for comparison, the batteries in many common electronic devices have a nominal voltage between 3 and 5 V). If two objects with different potential are brought close enough together, and their potential difference is sufficiently high, a spontaneous discharge of electrons called a spark will occur. This spark equalizes the potential between the objects as if they had been connected by a conductor. Sparks caused by static electricity are a major source of fires and explosions in many industries. Sparks release energy that can ignite flammable chemicals, industries where there is a lot of dust, like flour mills can also be at risk for explosions due to electrostatic sparks.
Not only can sparks cause an ignition or explosion, they can also cause serious burns or stop someone's heart.
Static hazards can be minimize by taking appropriate safety measures to control the accumulation of static charges. one of the important ways to control electrostatic buildup is by properly grounding and bonding equipment and containers.
In industry, static charge can be generated by machinery where there is any kind of friction or contact and separation, as well as in instances where there are rapid heat changes. People can build up their own charges simply by the friction created when they walk, so when they move within proximity to a machine, they can receive a shock or a spark can ignite flammable materials.
Some specific sources of static in industry will be discussed in more detail in this whitepaper. most static electricity in industry results from operations that involve friction, such as:
- Liquid or powder flowing through a pipe, hose or opening
- Blending or mixing
- Spraying or coating
- Filling operations
- Conveyor belts
Sources of Static Discharge
Operations
Piping Systems, Filling Operations and Loading / Unloading Liquids
Static electricity is generated when a low conductivity liquid (like oil or fuel) flows in a non-conductive pipe. This is especially dangerous when
loading or unloading trucks with flammable liquids. Negative charges accumulate on the pipe walls, while positive charges are carried away with the liquid. Since the pipe is not conductive, it cannot dissipate the electrostatic charge, so it remains on the pipe wall. If there is flammable air in the pipe, it can be ignited by a discharge, commonly near the end of fill pipes at the filling point.
The charges in the pipe also create an electrostatic field around the pipe. This means that other objects outside the pipe like gaskets, flanges, clips and bands can have a dangerous electrostatic potential unless properly bonded and grounded. Without proper grounding, discharges or sparks can jump from these objects to any conductive object of different potential, like grounded objects, tools or people.

Coating and Dispersing Operations
The coatings industry uses electrostatic charges to apply substances like paint, clear coat and powder coating to surfaces. This is especially common when painting cars, planes and appliances. In this process, a spray gun adds a charge to the paint or powder as it comes out. Since the plastic or metal being painted is grounded, it attracts the charged particles. This creates an even coat with less waste.
Proper grounding in this procedure is of the utmost importance, as there is a high charge generation which can cause sparking and ignition. Ignition on the spray gun when the substrate is not effectively grounded can cause the spray gun to shoot flames, as the highly charged spray substance catches fire from the spark.
Human Movement
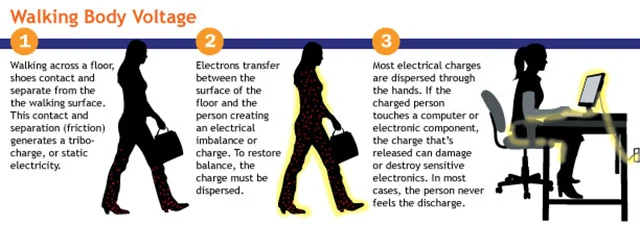
Any time two materials contact and separate, there is an exchange of electrons. This includes when a person is walking or moving: their arms rub against them as they walk, and their shoe soles interact with the floor's surface, generating an electrical charge that accumulates on their body. This is called walking body voltage.
As demonstrated in the previous video, the second a person touches an object, any potential difference between their body and that object is discharged.
If the object is an electrical component, the spark can interfere with the circuitry and destroy the component. A spark caused by this discharge is also a danger if in proximity to anything flammable.
Static Control Methods
Overview
The generation of static electricity cannot be stopped, but its rate of accumulation and dispersal can be controlled with proper engineering of machinery, pipes and filtration systems, as well as by utilizing proper bonding and grounding equipment. To help prevent the accumulation of static electricity in conductive equipment, the resistance of the path to Earth (ground) needs to be minimized.
Ground refers to a point of zero electric potential, so named because it is often taken to be the physical ground, or Earth. The electric potential of an object can only be understood in relation to another electric potential; for this reason, it is necessary to have a common reference point (ground) from which to define all voltages in a particular system. In the gravitational analogy, you cannot just specify that an object is 5 m high; you must also specify the point you started measuring from (coincidentally, ground is also an appropriate reference point here).
If an object has a non-zero voltage, it is separated from the ground in some way. If it is separated by a conductor, then electrons can flow between the object and the ground and there is a resistance between them. These three quantities--voltage, current (the flow of electrons), and resistance--are interrelated by a formula called Ohm's Law:
V=voltage, in volts
I=current, in coulombs per second, i.e., amperes
R=resistance, in ohms
One must work to dissipate static electricity by providing a path for electrons to traverse. A resistance of 1 megaohm or less is generally considered to be adequate for this path. When metal makes up the bonding/grounding system, the resistance will generally be less than 10 ohms. Any more than 10 ohms resistance means that the path to ground is not continuous, and is usually an indication of dirt, system fatigue, worn or loose connections and the possibility of system deterioration. Any grounding system that is considered acceptable for lightning protection or power circuit protection is plenty adequate for a static electricity grounding solution.
Some methods we will discuss for static control are:
- Bonding
- Grounding
- Humidity
- Additives
- Clothing and Materials
- Filling Speeds
Grounding And Bonding
Bonding and grounding are effective methods for managing and reducing static electricity and thus minimizing the possibility of electrostatic sparks or ignition. The difference between the two is that bonding connects two objects together, while grounding connects an object with the earth.
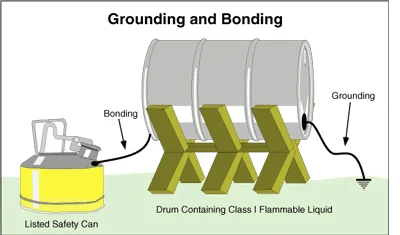
Bonding connects two or more pieces of conductive equipment together using wires, cables or other connectors in order to equalize their static charge. Sparks cannot occur between objects that are at the same electrostatic potential. Containers need to be connected even if they are touching, because paint or other coatings may reduce the conductivity Simply touching another object does not guarantee an effective connection for static charge to transfer.
Grounding (or Earthing) is the best and safest way to discharge built-up static charge. To ground an object is to connect it to the earth via a grounding rod or electrode stuck in the ground. Grounding drains the static charges away as they are produced, removing excess charge by transferring electrons between the object and the earth. In this case, conductive materials or objects are connected to the earth via wires, clips, cables and clamps. This is similar to bonding, except one of the objects is the ground itself.
Good connections are very important in grounding and bonding. Any object being grounded or bonded needs a conducting pathway for the charged electrons to travel along. Grounding prevents sparking between properly grounded objects and conductive equipment.
In potentially hazardous or flammable situations, all objects that are conductive but separated from ground by nonconductive equipment (like gaskets, hoses and piping, spray nozzles, thermometers and probes) should be bonded. When an item is isolated from either the ground or a bond, it can become charged enough to cause a static spark.

Grounding Assemblies, Cables and Clamps
Items such as drums and tanks can have their conductivity affected by paints, coatings or a buildup of product. These coatings can be thick enough to keep electrostatic charges from dispersing altogether, The solution is to use a grounding assembly with clamps that can pierce paint for a good metal-on-metal connection.
The photo to the left shows one type of Mueller grounding assembly with a paint-piercing clamp on one end and a copper clip on the other. Thee are many different configurations of grounding/bonding assemblies, including different types of clips, clamps and wire, which are selected based on the items and materials to bond/ground.
Some important criteria to remember when selecting a bonding/grounding assembly are:
- Does the item being grounded have a point or coating that needs to be pierced for a good connection?
- What's the environment that this is being used in? How rugged does the assembly need to be?
- What type of clip is needed? (flat, dimpled or with teeth?)
- Are the objects being grounded stationary or do they need to move?
- What length of wire is needed?
- Is clean-ability important?
- Does it need to handle heat?
- Should the wire be insulated or non insulated?
- Does the wire need to be conductive for additional current to be carried?
Humidity
Static has a tendency to build up more in dry environments because any moisture in the air can help disperse the static charge on an object. Increasing the humidity in an industrial environment is not always feasible, but it is an option to consider. It is advisable to maintain a humidity level above 60% through the use of different kinds of industrial humidifiers.
Additives
Antistatic additives to liquids like fuel can increase conductivity which can help in reducing electrostatic charge formation.

Materials, Flooring and Clothing
Conductive flooring, shoe soles and special clothing can dissipate static charges from a person as they walk and move.
The type of container (meta, plastic, etc) should be a safety consideration when storing and handling flammable materials. insulating and non-conductive materials increase the risk of accumulating a charge.
Pictured here is an antistatic floor mat from Crown Mats.
Controlled Filling Speed and Relaxation Time
The higher the speed of liquids, the higher the generation of static charges. Splashing, sprinkling and spraying should be avoided. Some operations may recommend a relaxation time depending on the substance being dispensed. Once dispensing is completed, it is best to wait before doing anything further to the equipment, such as opening or closing lids, cleaning or taking samples. This relaxation time depends on the type of liquid, however; one minute is considered acceptable for many liquids.
Summary
Contact Us For A Quote!
"*" indicates required fields