WHAT ARE THEY AND WHICH ARE BEST FOR YOUR PURPOSE?
With so many various types of M12 connections and options to choose from, such as pin count, pin positions, connection coding and IP ratings, the selection process can seem rather overwhelming. What does it all mean and how do you know which connections are right for your specific application? This article will explain these terms, what all of them mean as well as all of their classifications, so that you can discover which M12 connections are right for you.
M12 CONNECTIONS … WHAT ARE THEY?
What is an M12 connector? The name M12 came about pretty simply: M stands for the unit of measurement taken (in this case, metric) and 12 stands for the length of the diameter taken across the outside of the threads (12mm). M12s have circular connections and, because of their circular shape, they possess high current capabilities and are much easier in obtaining ingress protection (IP) ratings, or ratings that tell how well connections are able to keep out elements such as dirt, sand and water, than their rectangular counterparts. This makes them an excellent choice for use in factory automation applications, or in any tough or harsh environment where dirt or dampness is involved.
PIN COUNT
Choosing the right M12 connections depends on your specific application. M12 connections come in a variety of pin positions, anywhere from 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 12 and 17 pins. The number of pins varies depending on the signal type and number of signals, connection coupling and code.
Pin counts differ according to code. Connections with B code, which are used for Profibus connections, typically have 5 pins, although their pin count can vary from having 3-5 pins. Connections with C code, which are used for AC power applications, usually have 6 pins, although their pin count can also vary from 3-6 pins. Connections with D code, which are used for Ethernet applications involving data transfer of up to 100 Mbits, always have 8 pins. Connections with A code, on the other hand, are used as all-purpose connections in such a wide variety of factory automation applications, such as attaching to sensors, actuators and a number of other smart devices, that the pin count can be anywhere from 2-17 pins.
PIN POSITIONS AND CONNECTION CODING
Different pin positions have been created to coincide with the different types of coding that have been devel- oped according to function. This way the pin positions act as a fail-safe and eliminate any mistakes of cables being connected that were made for different coding. For instance, you would certainly connect cables that both have A-coding and are being used to hook up sensors with corresponding equipment, however; you would not want to connect an AC power cable to an Ethernet cable.
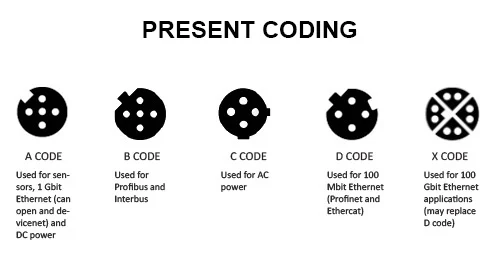
CODING FOR DATA APPLICATIONS
Below is a description of the different coding classifications currently used in factory automation and what they mean.
A-CODING
A-coding (also known as Micro-DC) for factory automation cables is the most widely used coding in factory automation applications of all the types. These connections are used in data applications primarily involving DC power. A-coding is used for attaching actuators, attenuators, sensors, motor-operated switches and other devices to automation equipment. A-coded connections are also used to transfer up to 1-Gbit of data in Ethernet applications and can have anywhere from 2 to 17 pin positions.
B-CODING
B-coding is unique in that it contains a reversed single keyway, which allows 2 unique M12 connections to be mounted on the same panel without the risk of incorrectly coupling connections to equipment with varying voltage and amperage. B-coding for factory automation cables is used in fieldbus connections involving Profibus and Interbus. B-coding connectors typically have anywhere from 3 to 5 pins.
C-CODING
C-coding (also known as Micro-AC) is strictly used in cases where AC current is involved, such as with AC actuators, sensors and other AC devices. Because of this C-coding is not as commonly used as the other coding types. Connections with C-coding all have extended grounding pins and double keyways for added safety to prevent them from being mistaken for other similar-looking connections or being coupled with the wrong cables. C-coding connections have anywhere from 3 to 6 pins.
D-CODING
D-coding is specifically used in network cables for industrial Ethernet applications to transfer data up to 100-Mbits. The insides of cables with this type of coding consist of either 4 wire connectors (D-coding) with 2 pairs of Cat 5e cables or else M12 8 wire (A-coding) connectors with 4 pairs of Cat 5e cable. D-coding can also be used with Profinet, Ethernet/IP and EtherCat systems. D-coded connections usually have 3 to 5 pins.
X-CODING
X-coding has been introduced in the recent years and is quickly becoming a standard for use with high-speed industrial Ethernet applications. X-coding has capabilities of transferring large amounts of data at high speeds, up to 10-Gbits of data. X-coding is expected to eventually replace A- and D-coded parts for Ethernet applications. X-coding applications include high-speed industrial Ethernet and Cat6A. X-coded connections always have 8 pins.
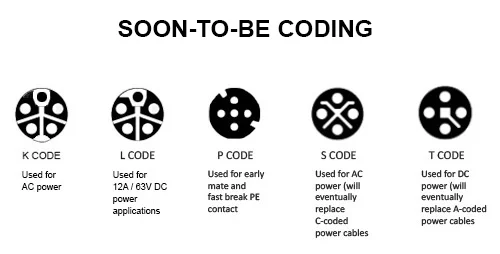
CONNECTION CODING FOR POWER APPLICATIONS
While A, B, C, D and X connection coding make up the majority of factory automation cable use today, new coding is being introduced as well. K, L, S and T coding are all used for power applications. Rapid advancements in Industry 4.0 technology have resulted in these codings providing improved performance in specific power operations. S- and K-coding are both used for AC power applications and it is believed that S-coding will at some point take the place of C-coding that is currently used. T- and L-coding are both used for DC power applications and it is believed that T-coding will at some point take the place of A-coding that is currently used. P-coding has also been developed for various uses where quick connects and disconnects of cables are needed.
IP RATINGS
As mentioned earlier, the circular shape of M12 connectors makes it easy to assign them IP ratings which classify how well connectors are able to block out unwanted elements that can cause corrosion and other problems. Because of the rugged design of M12 connections, they are an ideal choice for use in factory automation.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) came up with these rating classifications and international standards which set the bar for what connections can withstand. There are three common IP standards associated with M12 connections which are IP67, IP68 and IP69.
What are the differences?
The first digit (in this case, the number 6 in all three ratings given) refers to the connection’s resistance to solid objects, such as dirt, sand or dust. The significance of the number 6 means that after being in contact with solids for 8 hours, the connection does not absorb any “harmful” dirt and it is still functional. The second digit refers to the connection’s resistance to water. In the examples given we have 7, 8 and 9.
The significance of the number 7 means that the connection can be submerged in a greater depth of up to a 1 meter of fresh water for half an hour and still be water resistant. The significance of the number 8 means that the connection can be submerged in up to 1.5 meters of water for a half an hour and still be resistant. The significance of the number 9 means that the connection can actually withstand high pressures, high-pressure jet sprays, wash downs and steam cleaning procedures.
MAKING YOUR SELECTION
Now that you know about pin counts, pin positions, coding and ratings, you are ready to select your connections. Mueller Electric can help you with the process. Mueller Electric’s M12 factory automation connections have the most reliable and efficient connection standards for industrial machinery and industrial automation applications. Having high-performance capabilities, small footprints and extremely low failure rates, Mueller Electric’s connections are ideal for use in the toughest conditions.
Mueller Electric offers M12 cable connections with features such as:
Industry-standard screw-locking mechanisms
IEC ratings of IP67, IP68 & IP69
A, B, C, D & X-coding options
Field-installing cable and panel-mount options
Moulded straight and right-angle variants
Pin ranges of 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 12 & 17 positions
Shielded PVC and PUR options for cables
What’s more, if your automation takes place in a moist environment or if your equipment requires washdowns, factory automation cables with a minimum IP rating of IEC-IP68 are recommended. These cables provide a strong, secure and sealed connection between your automation equipment and robots, sensors, actuators, machine vision systems, motor-operated switches and other smart components, even in humid or moist conditions. The IEC-IP68 rating is highly recommended for factory automation in both the food and beverage and measurement and control industries. The IEC-IP69 rating is what is most often used in road vehicle applications. All of Mueller Electric’s M12 connections have an IEC ratings of IP67, IP68 and even IP69, the highest IEC rating available.
CONTACT MUELLER ELECTRIC
Still have questions about what an M12 connector is? Give Mueller Electric a call at 800.955.2629 or contact us here. One of our knowledgeable staff members will be happy to help you select the connections that are best for you. With a wide array of factory automation connections, including a large selection of UL-listed connections in our factory automation catalog, Mueller is sure to have something for everyone. If by chance you do not see what you are looking for, Mueller also specializes in creating custom-made cable orders and can put together a solution just for you and your unique application needs!
For more information on M12 connections, feel free to visit Mueller Electric at www.muellerelectric.com.
