M12 CABLES: CODING FOR TODAY AND TOMORROW
Have you wondered about the different cable coding types for instrumentation cables and what they mean?
M12 cables have come in a variety of coding options and each code is used for a specific application. Simply put, M12 codes are designed to keep cables mating with the correct connections to ensure that, for example, an AC power cable is not being hooked up with an Ethernet cable.
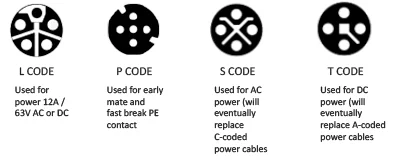
From the outside, connector housings look the same but when you consider the internal configurations of the M12 connector, things are quite diverse. Most users of M12 cables are familiar with codes A through D and possibly X. There is more cable coding in addition to these and some have been designed to replace existing codes. Below are keyways commonly used today. Below that are keyways less well known that may become more prominent in the future.
How do you know which code is right for you? With our cable selection guide, feel free to look through our assortment of instrumentation cables and their related coding to see which best fits the application needed. If you still have questions or don’t see what you’re looking for, feel free to contact me at 800.955.2629 to discuss what you want to accomplish and I can assist you in finding the right cables. On the rare chance you don’t see what you’re looking for, Mueller Electric can always create custom cables based on your company’s specific needs.
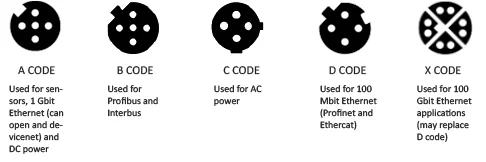
A-coded connectors are the most common type of keyways and are used with sensors, actuators, attenuators, motors and other devices. B-coded connectors are most often used in network cables for fieldbus connections. C-coded connectors are used mainly with AC sensors and have a dual keyway for security, used to make sure no other cable is accidentally used in place of a C-coded cable. D-coded connectors are generally used for Ethernet and can transfer data up to 100 Mb. X-coded connectors are becoming more popular due to their ability to transfer large amounts of data, up to 1 Gb, at high speeds.